

They are usually black or dark brown in color and have a shiny, almost greasy appearance. Oriental cockroaches, on the other hand, have a rounder, more robust body shape with shorter legs that are adapted for crawling. They are usually brown or black in color and have a streamlined shape that helps them move through the water more easily.
Water bugs have a flattened, oval-shaped body with long, slender legs that are adapted for swimming.
Physical Characteristics: Water bugs and oriental cockroaches differ in their physical appearance as well. Oriental cockroaches are scavengers that feed on a variety of organic matter, including decaying plant material, garbage, and even dead insects. They are not aquatic insects and cannot swim. In contrast, oriental cockroaches are a type of urban pest that prefers dark, damp environments such as sewers, basements, and crawl spaces. Water bugs are also predatory insects, feeding on other aquatic creatures such as small fish, tadpoles, and insect larvae. They have adapted to life in the water and are excellent swimmers, using their long legs to glide across the surface of the water. Habitat and Behavior: Water bugs, as their name suggests, are primarily aquatic insects that live in bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, and streams. However, there are several key differences between the two that set them apart. Water bugs and oriental cockroaches are two distinct types of insects that can sometimes be confused due to their similar appearance. In such cases, it may be necessary to control their populations using physical or chemical methods. However, some types of water bugs can be a nuisance to humans, particularly if they invade swimming pools or other areas where people gather. They also serve as indicators of water quality, as certain species are sensitive to pollution and other environmental stressors. Water bugs play an important role in aquatic ecosystems, both as predators and as a source of food for other organisms. Giant water bugs are also capable of delivering a painful bite to humans if they are mishandled. They are powerful predators that feed on fish, amphibians, and other aquatic insects. Giant water bugs are some of the largest aquatic insects in the world, with some species reaching lengths of up to 4 inches (10 cm). One example is the giant water bug, which belongs to the family Belostomatidae. There are also several types of aquatic beetles that are commonly referred to as water bugs. Water striders feed on insects and other small organisms that fall onto the water's surface, using their sharp mouthparts to pierce and suck out the prey's fluids. This allows them to stand on the surface of the water without breaking the surface tension. Water striders are easily recognizable by their long, slender legs, which are covered in tiny hairs that repel water. Water scorpions are also able to breathe air using a specialized tube that extends from their abdomen to the surface of the water.Īnother type of water bug is the water strider, which belongs to the family Gerridae. They use their elongated front legs to capture prey, which includes small fish, insects, and even other water scorpions.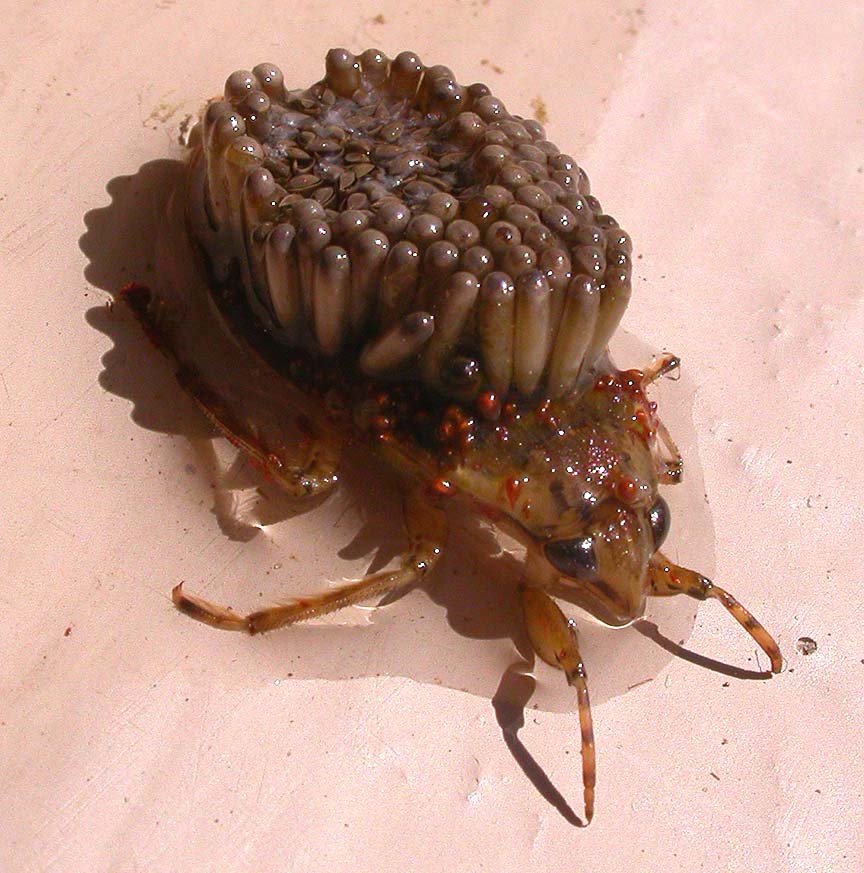 
Water scorpions are typically brown or green in color and have a long, narrow body that resembles a stick or a twig. One common type of water bug is the water scorpion, which belongs to the family Nepidae. In general, water bugs are known for their ability to glide across the surface of the water using specially adapted legs, and for their predatory feeding habits. There are several different types of water bugs, each with unique physical characteristics and behaviors.

A water bug is a type of insect that is commonly found in aquatic environments, including lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
